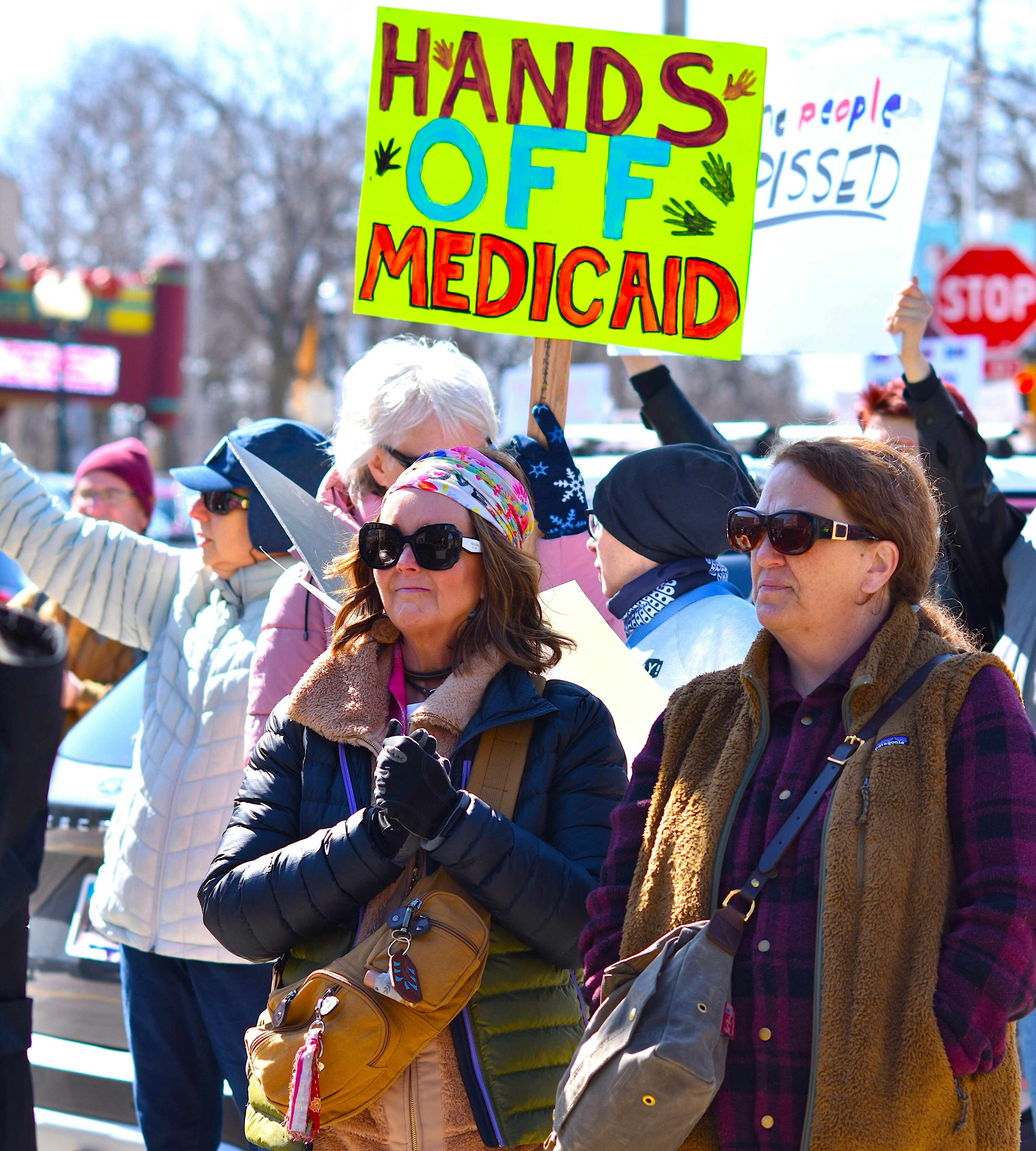Marisol Pantoja Toribio found a lump in her breast in early January. Uninsured and living in California without legal status and without her family, the usually happy-go-lucky 43-year-old quickly realized how limited her options were.
“I said, ‘What am I going to do?’” she said in Spanish, quickly getting emotional. She immediately worried she might have cancer. “I went back and forth — I have [cancer], I don’t have it, I have it, I don’t have it.” And if she was sick, she added, she wouldn’t be able to work or pay her rent. Without health insurance, Pantoja Toribio couldn’t afford to find out if she had a serious condition.
Beginning this year, Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program, expanded to include immigrants lacking legal residency, timing that could have worked out perfectly for Pantoja Toribio, who has lived in the Bay Area city of Brentwood for three years. But her application for Medi-Cal was quickly rejected: As a farmworker earning $16 an hour, her annual income of roughly $24,000 was too high to qualify for the program.
California is the first state to expand Medicaid to all qualifying adults regardless of immigration status, a move celebrated by health advocates and political leaders across the state. But many immigrants without permanent legal status, especially those who live in parts of California where the cost of living is highest, earn slightly too much money to qualify for Medi-Cal.
The state is footing the bill for the Medi-Cal expansion, but federal law bars those it calls “undocumented” from receiving insurance subsidies or other benefits from the Affordable Care Act, leaving many employed but without viable health insurance options.
Now, the same health advocates who fought for the Medi-Cal expansion say the next step in achieving health equity is expanding Covered California, the state’s ACA marketplace, to all immigrant adults by passing AB 4.
“There are people in this state who work and are the backbone of so many sectors of our economy and contribute their labor and even taxes … but they are locked out of our social safety net,” said Sarah Dar, policy director at the California Immigrant Policy Center, one of two organizations sponsoring the bill, dubbed #Health4All.
To qualify for Medi-Cal, an individual cannot earn more than 138% of the federal poverty level, which currently amounts to nearly $21,000 a year for a single person. A family of three would need to earn less than $35,632 a year.
For people above those thresholds, the Covered California marketplace offers various health plans, often with federal and state subsidies, yielding premiums as low as $10 a month. The hope is to create what advocates call a “mirror marketplace” on the Covered California website so that immigrants regardless of status can be offered the same health plans that would be subsidized only by the state.
Despite a Democratic supermajority in the legislature, the bill might struggle to pass, with the state facing a projected budget deficit for next year of anywhere from $38 billion to $73 billion. Gov. Gavin Newsom and legislative leaders announced a $17 billion package to start reducing the gap, but significant spending cuts appear inevitable.
It’s not clear how much it would cost to extend Covered California to all immigrants, according to Assembly member Joaquin Arambula, the Fresno Democrat who introduced the bill.
The immigrant policy center estimates that setting up the marketplace would cost at least $15 million. If the bill passes, sponsors would then need to secure funding for the subsidies, which could run into the billions of dollars annually.
“It is a tough time to be asking for new expenditures,” Dar said. “The mirror marketplace startup cost is a relatively very low number. So we’re hopeful that it’s still within the realm of possibility.”
Arambula said he’s optimistic the state will continue to lead in improving access to health care for immigrants who lack legal residency.
“I believe we will continue to stand up, as we are working to make this a California for all,” he said.
The bill passed the Assembly last July on a 64-9 vote and now awaits action by the Senate Appropriations Committee, Arambula’s office said.
An estimated 520,000 people in California would qualify for a Covered California plan if not for their lack of legal status, according to the labor research center at the University of California-Berkeley. Pantoja Toribio, who emigrated alone from Mexico after leaving an abusive relationship, said she was lucky. She learned about alternative health care options when she made her weekly visit to a food pantry at Hijas del Campo, a Contra Costa County farmworker advocacy organization, where they told her she might qualify for a plan for low-income people through Kaiser Permanente.
Pantoja Toribio applied just before open enrollment closed at the end of January. Through the plan, she learned that the lump in her breast was not cancerous.
“God heard me,” she said. “Thank God.” (Jasmine Aguilera/KFF Health News)
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism.